What is skin flora?
The skin flora is the types of microorganisms which reside on your skin. They are frequently referred to as the skin microbiome or skin microbiota.
Your skin has large numbers of these microorganisms on it. In total, there are 10 times more microorganisms than your own body cells!
Your skin hosts more microorganisms on your skin than anywhere else on your body, apart from your gut. Though bacteria are the most numerous of these microorganisms, mites, viruses and fungi also form a part of the skin microflora of a normal healthy human.
Human microbes
In brief, the microbes found on human skin are categorized into three groups:
1. Transients
These microorganisms are found intermittently on the human skin. They either don’t replicate or their growth rates are so low that they are not capable of sustaining their presence on the skin. Occasionally, they may only be isolated in cultures of skin samples and include Gram-positive bacteria such as clostridia which are found in the perineum.
A variety of factors influence transient skin microflora including skin characteristics such as pH, and dryness of the skin. Hot, humid weather conditions also lead to an increased number of transient microflorae on the skin. Similarly, personal hygiene is also a factor as unclean persons tend to have a greater number of transient microflorae. Age, too, plays a role and children tend to have a higher number of transient microflorae than adults.
2. Temporary residents
These microorganisms can maintain a growth rate that allows them to remain on the skin for a short duration.
3. Resident microorganisms
Resident microorganisms inhabit your skin permanently. They are considered true, normal, skin microflora. They’re able to survive, multiply and live on the skin. Usually, resident microorganisms are present in the upper part of the epidermis and are clustered in and around hair follicles.
It is presumed that resident skin microflorae have evolved in the skin’s environment. These include mainly gram-positive bacteria such as propionibacterium, brevibacterium, and others. Gram-negative bacteria are also resident bacteria and are present on your skin in limited areas. As an example, a resident microorganism that is highly prevalent on the skin is a yeast known as Malassezia.
How does skin flora come to the body?
The ecology of the skin surface drives the colonies of various microorganisms. However, this is variable and depends on the topographical location, external environmental factors and internal host factors.
Age has a huge effect on the microflora present on the skin. In the uterus, a fetus’s skin is sterile, but colonization from microorganisms occurs immediately post birth if the child is delivered vaginally. Organisms found in the mother’s vaginal canal colonize the baby’s skin. This also occurs a few minutes after birth if the child is delivered by Cesarean delivery. (The baby’s skin is colonized with organisms that reside on the mother’s skin)

The child receives most of the good microorganisms (both for the skin and the gut) from the mother and the environment at the time it is born. For this reason, many nurses and hospitals prioritize breastfeeding and contact of the baby’s skin to the mother’s skin during the initial months post delivery. This also helps in building the baby’s natural immunity through the mother’s skin and body microbes. The microflorae are also acquired through contact with the surroundings during daily life, for instance, animals, plants, chemicals and people.
During the first few years of life, the microbial communities on the skin establish and stabilize themselves as the newborn baby explores his environment and his immune system matures.
Where on the human skin is microflora found?
Skin is an organ of the human body that helps to protect us from environmental pathogens and reduces excessive water loss from the body at the same time. Some of its other functions include insulation, sensation, temperature regulation and vitamin D synthesis.
The skin consists of the epidermis, fat cells and dermis.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost skin layer. It provides a waterproof barrier that also creates the skin colour. The epidermis contains dead cells, which do not have nuclei. These cells are in constant contact with environmental microorganisms.
The epidermis does not allow these microorganisms to enter the skin’s deeper layers. It is usually impermeable to these microorganisms. However, cuts, wounds and abrasions on the skin’s surface may allow microorganisms to penetrate.
Dermis
The dermis lies underneath the epidermis and contains the connective tissues. It cushions the body from strain and heat and contains sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerve endings and hair follicles. Also, the dermis contains the lymph nodes and blood capillaries.
Sebaceous glands are present around the hair follicles and they produce an oily substance known as sebum, which lubricates the hair and the skin.
The sweat glands consist of long, hollow, coiled tubes. The coiled portion is located in the dermis and the long portion connects to a pore located on the outer surface of the skin.
There are two types of sweat glands: apocrine and eccrine glands.
- Eccrine glands are present all over the body, especially on the palms of the hands, forehead and soles of the feet.
- Apocrine glands are present in the groin, the underarms and around the nipples. They end in hair follicles instead of skin pores.
Hypodermis
The hypodermis helps to attach the dermis to the bones that lie beneath. It consists of connective tissues and fat. The functions of the hypodermis are to insulate and pad.
Skin microflorae are present all over the surface of the skin but the type of microorganism varies according to the anatomical site.
Three major types of skin sites:
- Dry
- Oily/ Sebaceous
- Moist
1. Dry sites of the body
Dry sites include the hands, legs, forearms and feet. The predominant organisms at these sites are Coagulase-negative staphylococci such as S. hominis and S. epidermedis.

2. Sebaceous or oily sites of the body
Sebaceous sites of the body include the neck, head and trunk, where the sebaceous glands situated in the skin secrete oily sebum. The major microflorae species found in these areas are Staphylococci and Propionibacteria. Demodex mites and the Malasezzia fungus are also present on the oily areas of the face.
3. Moist sites of the body
Corynebacterium and staphylococci are abundant in the moist areas of the folds of the skin including the elbow creases, the areas under the breasts, the groin, and areas in between the toes.
Does every person have the same microflora profile present on their skin?
Everyone has specific and unique skin microflorae contracted during infancy and that has stabilized during adulthood. Some variation occurs due to environmental factors and age. The microflorae of the skin change and the variety depends on the location. In addition, they vary according to the amount of light received by the area and whether the region is dry, moist, oily or hairy.
Moreover, the microflorae differ with gender and age. For example, a sweaty, hormonal boy in his teenage years has different microflorae on his skin to a sedentary female in her postmenopausal years.
After birth, the key factors that influence the presence of microflorae on the skin include the following:
- pH of the skin (normal pH of the skin is somewhat acidic at around 4-4.5)
- Moisture content of the skin
- Body temperature
- Ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- Sun exposure. Ultraviolet radiation damages microorganisms’ DNA.
- Interaction between different micro organisms present on the skin
- Internal defences of the host
- Genetic makeup of the host
- Kinds of personal and skin care products utilized
- Exposure to any medicines
- Exposure to other people
Three categories of skin microflora exist
1. Commensals
These are microorganisms which live on the skin and derive benefit from the host, but the host does not benefit from them.
2. Symbionts
Microorganisms which live on the skin, are beneficial to the host and also, in turn, derive benefit from the host.
3. Pathogens
Skin flora’s presence has certain unwanted consequences, even though most problems are minor and only present for a short duration. Some microorganisms present on the skin such as corynebacteria, kytococcus, and staphylococci contribute to the general body odour and odours that are specific to certain skin sites such as the axilla and foot. However, some can cause diseases. These include:
- Propionibacterium acnes causes acne
- Malassezia spp. causes folliculitis, pityriasis and dandruff
- Kytococcus sedenterius causes pitted keratolysis
- Corynebacterium spp. causes erythrasma and trichomycosis axillaris.
- The importance of Staphylococcus epidermidis is emphasized as it causes serious skin infections in hospitalized patients who undergo surgical procedures that involve the insertion of prosthetic implants and catheters. Immunodeficiency or immunosuppression further increases this risk.
Are the skin flora in a symbiotic relationship with humans?
According to a study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, microorganisms present on the human skin are usually considered as potential pathogens, pathogens or innocuous organisms that are in a symbiotic relationship with humans. Microorganisms present on the skin that very infrequently cause disease are called commensal. In other words, the microorganism lives peacefully on the host while getting benefit from it.
For instance, Staphylococcus epidermidis, which is a Gram-positive bacterium, is all along considered a commensal. But according to emerging evidence, this species of bacteria and other commensals may play a vital role in host defence. They are in a symbiotic relationship with humans instead of being commensals.
How do commensal microorganisms benefit us?
Commensal microorganisms may also help in the prevention of colonization of certain pathogenic microorganisms including S. aureus. Staphylococcus epidermidis produces compounds similar to antibiotics.
- Commensals reduce nutrients and make toxic compounds, thereby preventing the adherence of pathogenic bacteria to the skin cells.
- They boost the response of immune cells to pathogenic and harmful bacteria by producing cytokines, interferon and phagocytosis.
- Lipoteichoic acid present in the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria triggers the release of cathelicidin by mast cells. Cathelicidin is a type of antimicrobial peptide.
A 2013 study showed that there are even microbes in the subepidermal fat layers and not only on the skin surface. A healthy skin microflora protects from infection in a manner similar to healthy gut microflora – by overpopulating overgrowth of disease-causing microorganisms. Moreover, the skin microflorae prefer a slightly acidic pH (about 4-4.5) which prevents the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
Between the skin’s immune system and microflora
The skin’s immune system and skin microflorae regularly communicate with each other and control inflammation. When the microflorae are imbalanced, the skin’s immune system may release antimicrobial peptides, like cathelicidin, to help balance things out. Likewise, the skin microflorae may prevent the skin’s immune system from releasing inflammatory compounds.

Research done on mice in 2017 suggested that during early infancy, microflorae present on the skin induce “tolerance” in the infants. This may decrease the incidence of autoimmune diseases in adulthood.
Exposure to antibiotics during infancy that damages the skin microflorae may disrupt the induction of tolerance and allow the development of autoimmune diseases later in life. Some studies point to a correlation between the health of the skin microflorae and the maintenance of overall immunity.
The relationship between skin health and skin flora
What are the characteristics of good skin?
Beautiful skin has the following qualities:
1. Even tone or colour
Consistent colour or an even tone is the first sign of a healthy and youthful skin. From a young age, the skin is capable of regulating its pigmentation naturally; thereby resulting in a healthy-looking and uniform tone. However, the only exception to this is freckles, which are due to genetics.
2. Even and smooth texture
Another feature of beautiful skin is an even, smooth texture that is devoid of bumps and other common skin problems such as acne, whiteheads, blackheads, scars and wrinkles.
3. Hydration
Keeping the skin moist and hydrated is essential to ward off fine lines and wrinkles. Dry skin may lead to scaling and flaking.
4. Normal sensations
A healthy skin should not make its presence felt. As a matter of fact, there should not be any uncomfortable or unusual sensations, such as tightness and dryness after washing the face. Some other abnormal skin sensations also include itching, stinging, burning, and pulling.
What are the characteristics of bad skin?
Some of the signs that the skin is in poor health are:
1. Uneven texture and/or blotchiness
An unhealthy skin has a blotchy, uneven texture. Light or dark coloured or red spots or circles may develop under the eyes.
2. Acne
The development of acne indicates that the skin is unhealthy. Acne may occur due to excessive oil production and clogging of the skin pores by dead skin cells.
3. Scaly, flaky skin
Dryness due to dehydration may result in scaly, flaky skin.
4. Abnormal sensations
Abnormal skin sensations may develop such as itching, burning, stinging, pulling, or tightness.
How is your skin flora able to maintain good skin?
In the same way that good bacteria present in our gastrointestinal tract (gut) have an impact on our general health, microbes present on the skin have an impact on the way our skin feels and looks. They also impact the skin’s ability to form a barrier between the body and the outside environment.
According to Toral Patel, M.D., a dermatologist based in Chicago, skin microflorae are vital for maintaining not only the health of the skin but also our overall health. Healthy skin microflorae can protect against skin infections by preventing the overgrowth of disease-causing microorganisms. Skin microflorae are also able to fight against environmental and external factors.
The skin flora is able to maintain skin health by doing the following:
- Helping in dampening inflammation
- Promoting wound healing
- Acting as a physical barrier to environmental toxins and some allergens
- Limiting exposure to UV radiation and allergens
- Minimizing oxidative damage caused by free radicals
- Keeping the skin moist and plump
Evidence exists that balanced skin microflora may be effective in fighting against certain skin cancers.
What are the factors affecting the well-being and quantity of skin flora?
The factors that affect the well-being of skin flora include:
Cosmetic use
Ingredients in makeup affect the skin’s surface and are absorbed into the skin. They may thus lead to subtle changes that can have a negative impact over time. For instance, certain common ingredients present in eyeshadows that are harmful to the skin microflorae are aluminium powder, coal tar, bismuth oxychloride, formaldehyde, parabens, nanoparticles, talc and thimerosal. If one uses these products on a daily basis, these ingredients can play a significant role in altering the natural skin florae.

Products for personal care
Moisturizers and lotions might harm the skin, especially if applied to almost every part of the body. Certain ingredients present in these creams play a significant role in altering the microflorae of the skin. Some of them can even cause endocrine disorders.
BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole), fragrances, DMDM Hydantoin, Triethanolamine and Retinyl Palmitate are a few common ingredients.
Antiperspirant is another product that is potentially harmful and is commonly used. The active ingredient in antiperspirants is aluminium, which kills the bacteria residing on the underarms and temporarily stops the production of sweat by the sweat glands. There are potential links between antiperspirant use and breast cancer but no solid evidence exists to prove them.

Anti-bacterial soaps
Most people practice basic hygiene and hand washing without giving it much thought. However, what you should pay attention to is the kind of soap you are using. Anti-bacterial and anti-microbial soaps destroy not only harmful bacteria but also the good ones.
Bacteria, on exposure to triclosan, (an ingredient that is present in the majority of antibacterial hand cleansers) undergo genetic mutation. This mutation makes bacteria resistant to these compounds. Gradually they may become tolerant to certain antibiotics also.
Food sensitivities
Dairy and gluten are linked to skin diseases such as psoriasis and eczema. Healing the gut promotes overall health including skin health.
Host factors
Host factors such as age, sex and location play a huge role in the diversity of skin microflora.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors that are specific to a person such as choice of clothing, occupation and antibiotic use may modulate how the microflorae colonize their skin. Cosmetics, hygienic products, moisturizers and soaps are also factors that contribute to variations in skin microflorae.

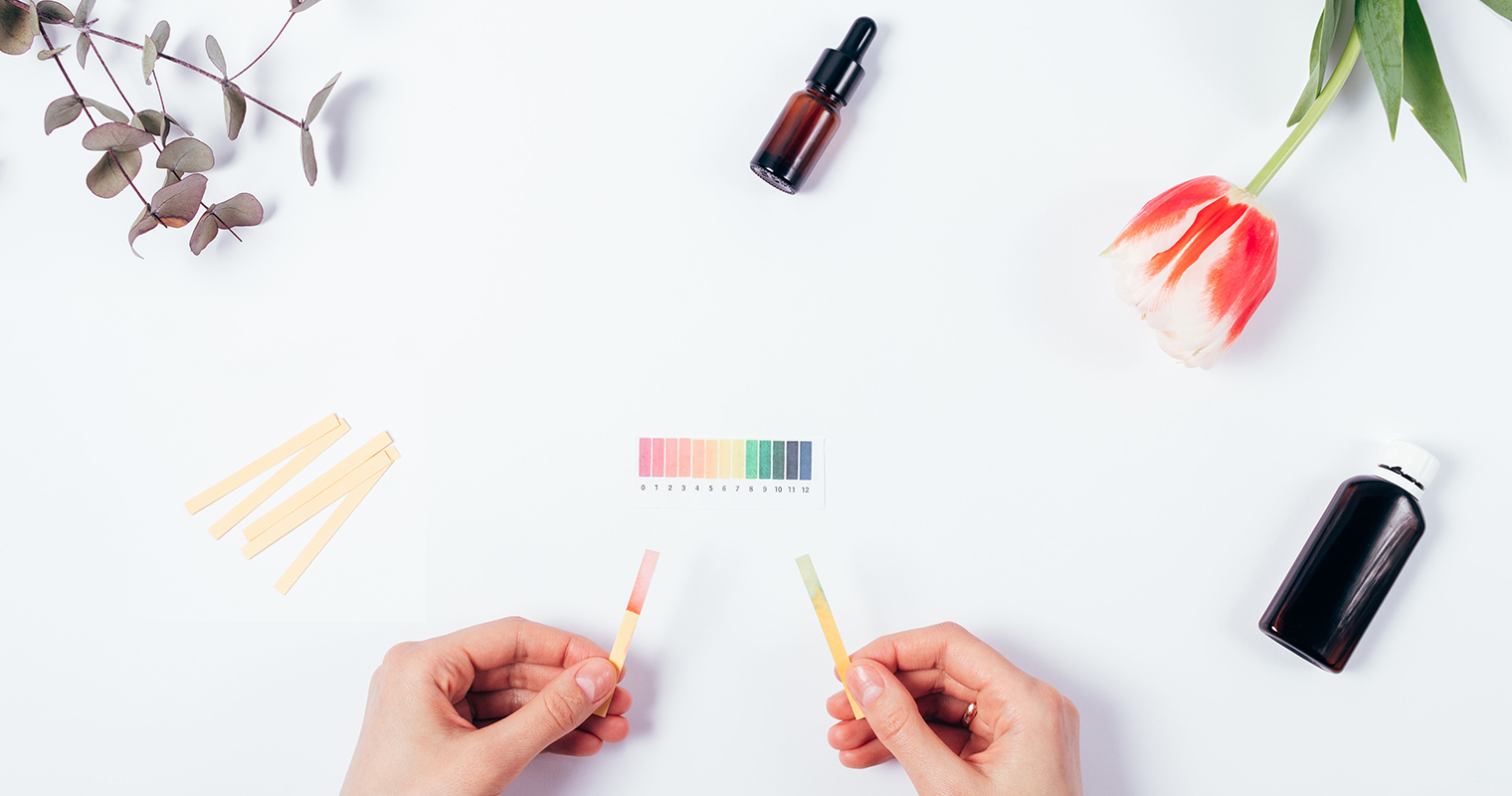
According to a study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science, the natural pH of the skin surface is on average below 5 (4-4.5), which keeps the resident microflorae attached to the surface of the skin. The study also demonstrated that an alkaline pH (8-9) promotes the dispersal of microflorae from the skin.

What can we do to maintain the well-being of our skin flora?
Given that skin microflorae play such a vital role in the maintenance of our appearance and health, it’s important to take appropriate steps to their health.
You can do the following to maintain a healthy skin microbiome:
Get out as much as possible
Spend some time outside of the house regularly. The ideal situation would be where you get dirty or are around animals. However, even a walk in the park may expose you to new kinds of microbes which may transfer to the skin and diversify or replenish your microbiome.

Relax often
Your body is not able to tolerate prolonged stress, and your skin is not an exception. Do things to manage stress so that your skin microorganisms can flourish. Some great ways to reduce stress include starting a gratitude or meditation practice, avoiding foods which tend to raise stress levels such as those that contain sugar or caffeine, practising yoga and limiting screen time.

Embrace your own skin
People usually get into their beauty and health routines pretty early in life, implying that they may not have the knowledge of whether they are right for the skin or not. Give your skin a break from the routine facial regimen you normally undertake. Experience how your skin feels without a multitude of products on it.
Clean out your cosmetic cabinet
Get rid of all beauty and cosmetic products which contain ingredients that may have the potential to deplete your skin’s microflorae. It’s best to avoid any products that read “antimicrobial” or “antibacterial” on their label and also to avoid products that contain ingredients including mineral oil, petroleum and its byproducts, parabens and propylene glycol. Even so-called “natural” products may contain certain unwanted ingredients.
Be sure to read their labels carefully.
Give your skin microflorae a boost, both inside and outside
You may apply various things to your skin to change its looks temporarily, but for permanent, natural beauty and health you must go deep inside. Supporting the gut microbes is the best area, to begin with. Ensure you take a high-quality probiotic daily, drink plenty of water, eat lots of prebiotic-rich, organic foods, exercise regularly and spend time outside.
Moreover, since the microflorae of your skin are so vital to the radiant glow on your face, you may want to give them additional support by using skincare products enhanced with probiotics. You can either go for a premium probiotic-containing skincare regimen or get a yummy yoghurt facial. You may also apply a powdered probiotic mixed with shea butter or coconut oil to your skin.
Probiotics may help to protect your skin from environmental toxins when applied directly to the skin. Besides soothing temporary skin inflammation, they also help in bringing back the balance of your skin’s microbiome.

Minimize the use of soaps and hand sanitizers
Don’t use antibacterial soap on your skin. Try natural, non-toxic cleansers and moisturizers instead.
Exercise regularly and get sweaty
If you are eating a good diet, the sweat produced during exercise will act as food for your skin’s microflorae. Sweat acts in a similar way to how prebiotics works for gut bacteria. You can also get sweaty by spending some time in a sauna.

How and what to eat for good skin flora?
Consume clean foods rich in fiber as they are a rich source of prebiotics
Prebiotics are a source of fibrous carbohydrates, which nourish the gut microflora and help them grow. A healthy gut microflora leads to healthy skin flora. Some examples of prebiotic-rich foods are asparagus, legumes, onions, oats, bananas, garlic, soybeans, and Jerusalem artichokes.
Eat foods rich in probiotics every day
You should eat a minimum of one serving of a probiotic or prebiotic-rich food per day. Some examples of probiotic-rich foods are fermented foods including yogurt, tempeh, kefir, and kimchi.
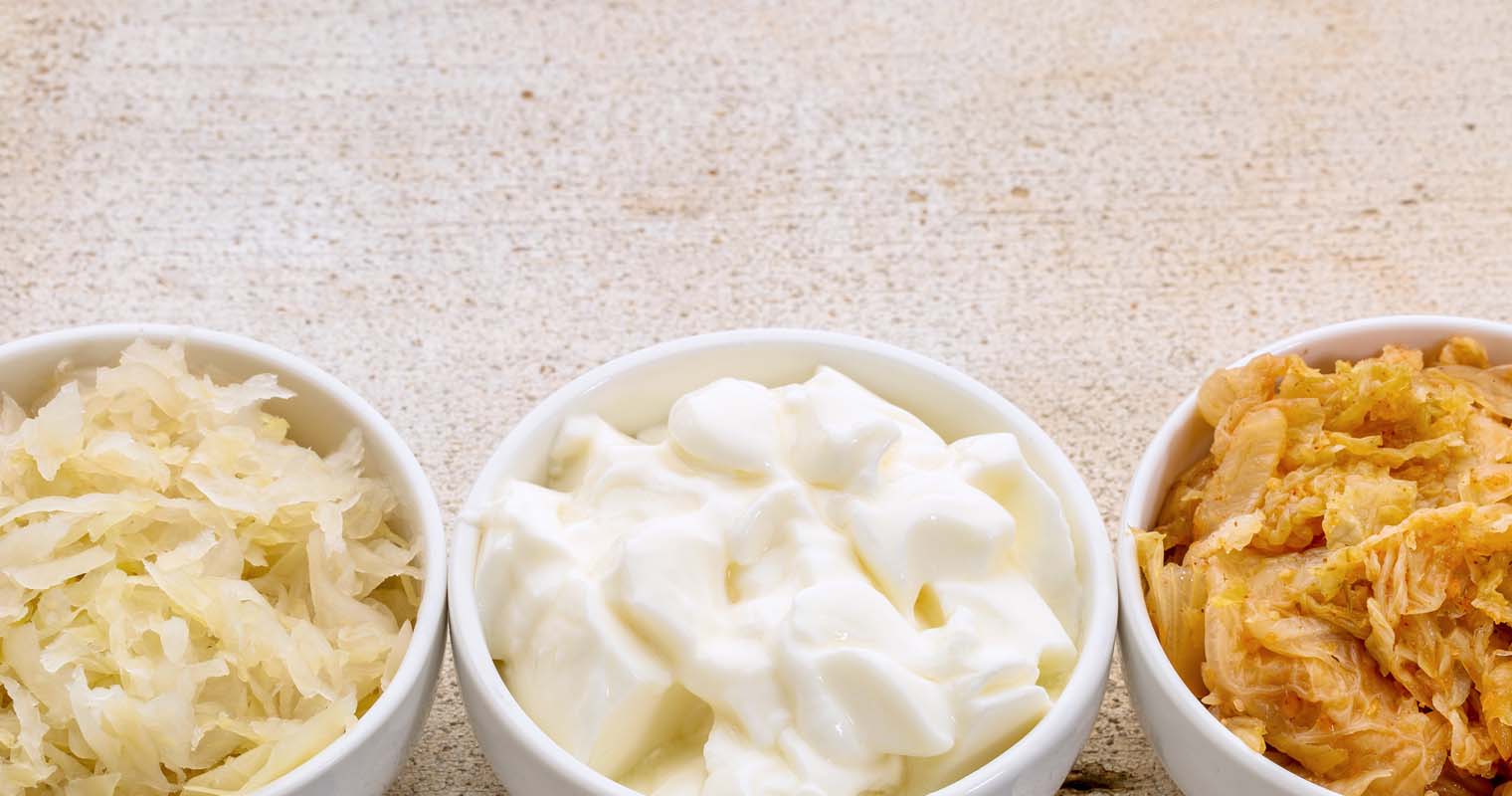

Eat foods rich in polyphenols
They help in improving your gut microflora, which promotes the health of skin microbiome. Some examples of foods rich in polyphenols are green tea, red wine, blueberries, and dark chocolate.
Include a probiotic supplement in your diet
You may take a daily probiotic supplement of high quality as there is much research to prove that use of probiotics helps in treating and preventing multiple skin conditions.
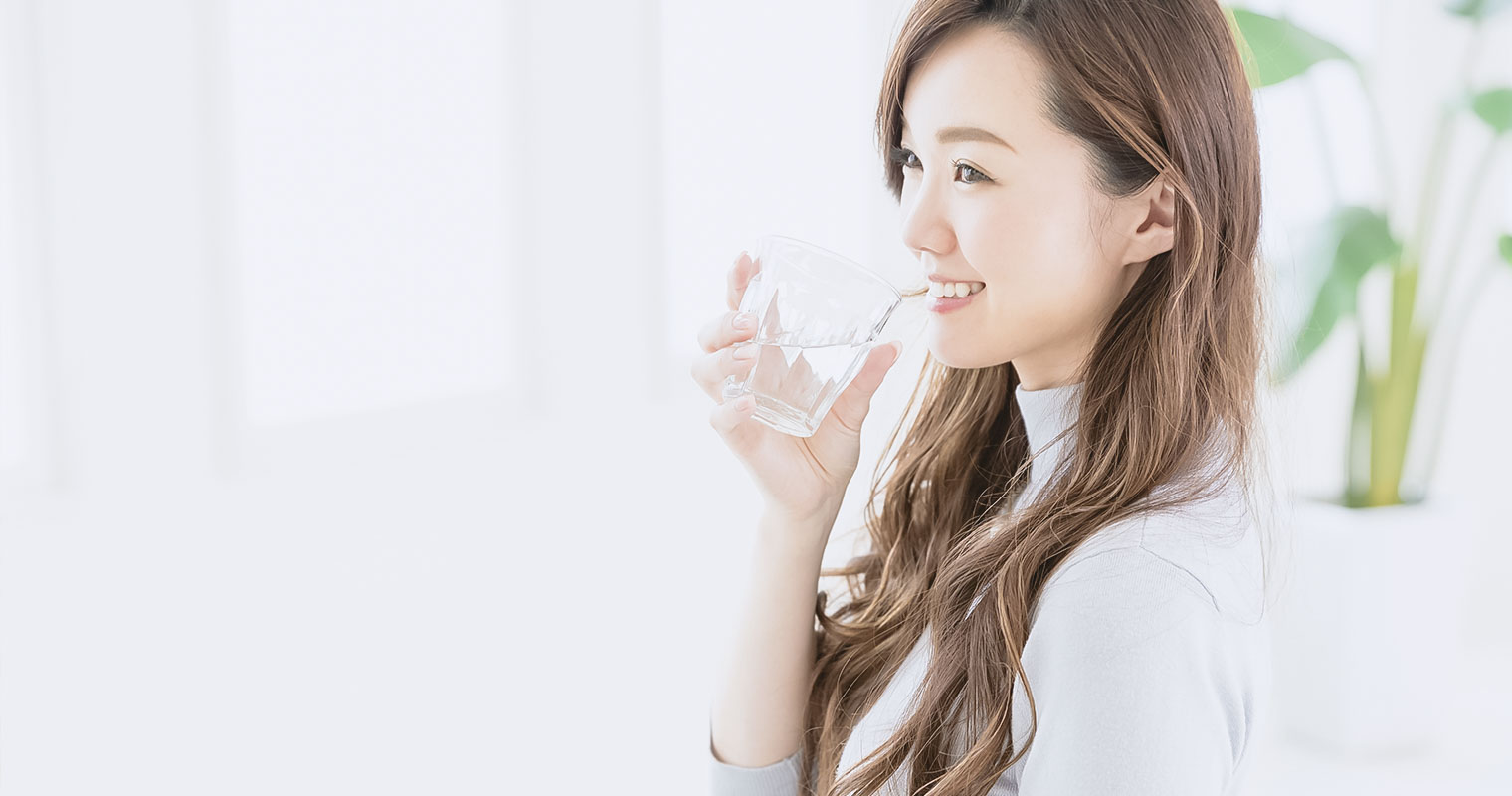
Stay hydrated
Drink lots of water to stay hydrated. According to research, drinking enough water and staying hydrated influences the skin microbiome.

Identify trigger foods and remove them
There are certain foods that may exacerbate a variety of skin conditions such as acne and eczema. Some examples of such foods are gluten and dairy. Identify what triggers your skin condition and remove them from your diet.

Rebalance skin microbiome by keeping your gut healthy
Maintain the health of your gut by eating a healthy diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics. This helps in maintaining a healthy gut microflora, which promotes the health of your skin microflora.
What foods to eat for good skin flora and a healthy skin?
Some of the foods that you should eat to maintain the health of your skin flora and; hence, skin in general is:
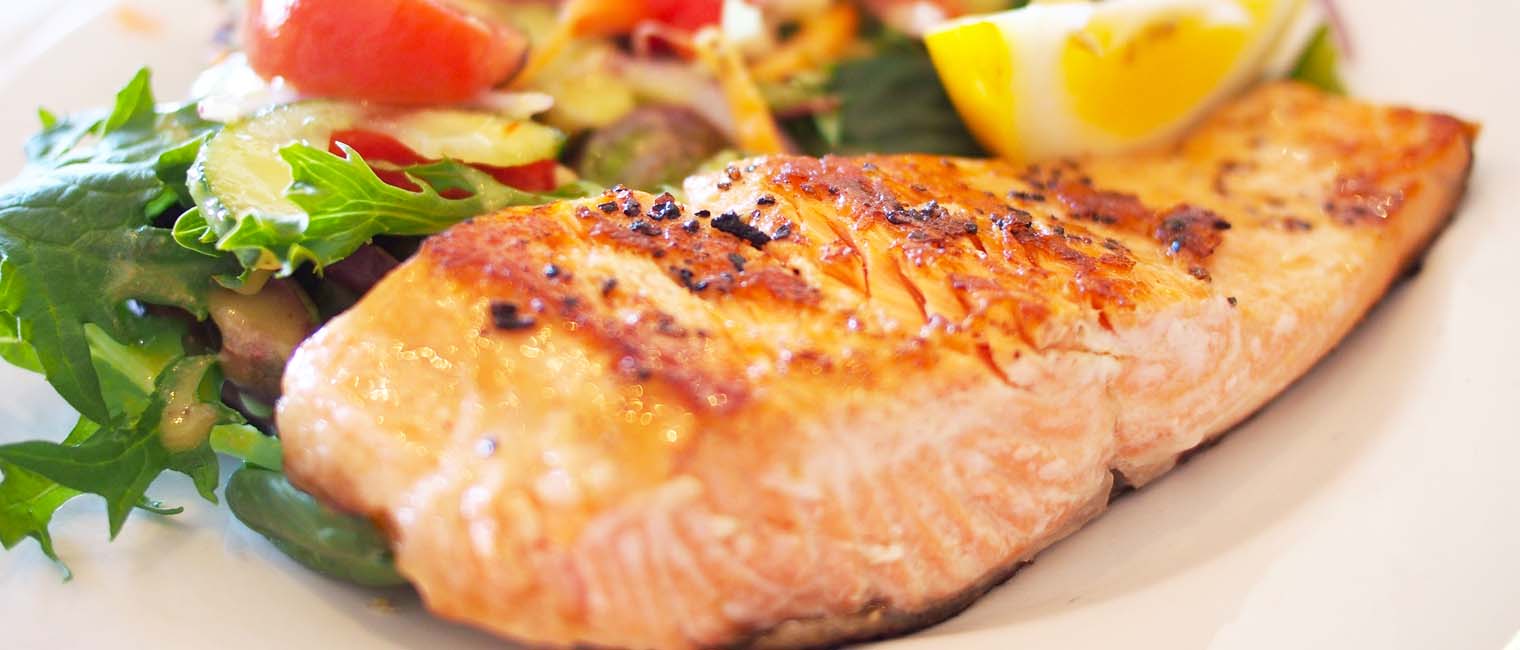
Fatty fish
Fatty fish including mackerel, herring, and salmon are all excellent to maintain the health of your skin. They contain a large amount of omega-3 fatty acids that are essential to keep your skin moisturized, supple, and thick. It helps in reducing inflammation that may cause acne and redness. Fatty fish also provides vitamin E, an important antioxidant that protects your skin from damaging free radicals. It also provides zinc that is vital for the overall health of your skin. In a study, it has been found that women who consumed more omega-3 fatty acids that are present in fish oil had a healthier and diverse gut flora. A healthy gut microflora is associated with a healthy and abundant skin microflora.

Walnuts
Walnuts contain a high amount of essential fatty acids, both omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Since walnuts have an excellent ratio of both these fatty acids, they can help in fighting the inflammatory response your body may have to an excessive amount of omega-6 fatty acids. Walnuts also contain zinc that is vital for the skin to maintain its barrier function and for the healing of wounds and combating inflammation and bacteria. They also contain small quantities of the antioxidants selenium, vitamin C, and vitamin E. Walnuts are also a rich source of dietary fiber and they help in promoting the health of gut microflora; thereby, the skin microbiome.

Avocados
Avocados are a rich source of healthy fats, which maintain the health of the skin by keeping it moisturized and flexible. They also contain compounds, which may protect the skin from the harmful rays of the sun. They are also a rich source of the antioxidants vitamin E and vitamin C both of which protect the skin from damaging free radicals. Avocados are also a rich source of fiber that feeds the gut flora keeping them healthy. This also helps in maintaining the health of your skin microbiome.

Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes are a rich source of beta-carotene, a nutrient (carotenoid) that functions as a precursor to vitamin A. Beta-carotene is an antioxidant that acts as a sunblock by getting incorporated into the skin. By protecting the cells of the skin from exposure to the harmful rays of the sun, it helps in preventing sunburn, death of the cells, and wrinkled, dry skin. Sweet potatoes contain resistant starch that acts just like fiber and escapes digestion and feeds your gut microflora. Hence, it helps in supporting the health of both gut and skin microflora.

Sunflower seeds
Generally, seeds and nuts are a rich source of nutrients to boost the health of your skin. A good example of this is sunflower seeds. They contain a large number of various nutrients including the antioxidant vitamin E, minerals zinc and selenium, and proteins.

Yellow or red bell peppers
Similar to sweet potatoes, yellow and red bell peppers are also a good source of the carotenoid beta-carotene, the precursor of vitamin A in the body. They also contain a large amount of vitamin C that is essential for the production of collagen; the protein, which keeps your skin strong and firm. According to a study, women who ate lots of vitamin C had a decreased risk of dry and wrinkled skin due to age.

Broccoli
Broccoli is a rich source of many minerals and vitamins that are vital to maintaining the health of your skin including vitamin A, vitamin C, and zinc. It is also packed with Lutein, which is a carotenoid similar to beta-carotene. Lutein helps in protecting the skin from free radical damage (oxidative damage) that may make your skin wrinkled and dry. Broccoli is also a rich source of a special ingredient called sulforaphane that has some impressive benefits for your skin. It may even possess anti-cancer effects and helps in preventing certain kinds of cancers of the skin. It can also work as a potent protective agent against damage caused by the sun. It may also help in maintaining the levels of collagen in the skin. Broccoli also contains certain compounds that are used by the friendly bacteria of the gut and which improve the overall health of the gut. By promoting the health of the gut microflora they promote the health of skin microbiome.

Soy
Soy is a rich source of isoflavones, a type of plant compounds, which can either block or mimic estrogen in the body. They may provide benefits to various parts of the body including the skin. According to a study it was found that consuming soy isoflavones regularly for eight to 12 weeks helps in reducing fine lines and improving skin elasticity in middle-aged females. In postmenopausal females, soy also helps in improving the dryness of the skin and increasing collagen; thereby keeping the skin strong and smooth. The isoflavones present in soy also protect the skin from the damaging rays of the sun and help prevent certain skin cancers. Soy and soy products are a rich source of probiotics which help to promote the health of your gut flora and a healthy gut flora is associated with a healthy skin microbiome.

Tomatoes
Tomatoes contain a large amount of vitamin C and are a rich source of all of the important carotenoids including Lutein, Lycopene, and beta-carotene. These carotenoids may protect the skin from damage caused by the harmful rays of the sun and also prevent wrinkling of the skin. Since all the important carotenoids are present in tomatoes, they form an excellent food to maintain the health of your skin. It’s a good idea to pair foods rich in carotenoids such as tomatoes with fat-rich foods such as olive oil or cheese. This is due to the fact because fat increases the absorption of carotenoids in the intestines.

Dark chocolate
The effects that eating cocoa has on the skin are quite phenomenal. In one study the participants experienced more hydrated and thicker skin after eating cocoa powder rich in antioxidants every day after a period of six to 12 weeks. Their skin also became less scaly and rough, was less sensitive to damage by sun, and had improved flow of blood. In another study, it was found that consuming 20 g of dark chocolate containing a large number of antioxidants every day can help the skin to tolerate about two times UV rays before burning than eating chocolate containing a low amount of antioxidants. Similar results are found in several other research studies including improvement in skin wrinkles. Furthermore, your gut bacteria, such as lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacterium ferment dark chocolate and feast on it. Hence, it improves the health of gut bacteria; thereby the skin microflora. But make sure that you eat dark chocolate containing a minimum of 70 percent cocoa with minimum added sugar to get maximum benefits.

Red wine
Red wine is a rich source of Resveratrol, an ingredient that is derived from the skin of grapes (red). Resveratrol produces a wide variety of health benefits including decreasing the harmful effects of aging. According to studies, it may help in slowing the production of free radicals that may damage cells of the skin and cause visible signs of aging. The polyphenols present in the red wine also have a positive effect on the intestinal bacteria and a balanced intestinal flora indicates a healthy skin microflora. Unfortunately, not enough evidence exists to prove the fact that whether the quantity of Resveratrol present in one glass of red wine is sufficient or not to impact the health of your skin. Moreover, as red wine is alcoholic it may produce negative effects if taken in excessive quantity. It is not advised that you start consuming red wine due to its potential benefits to your health. But if you drink it in moderate quantities already, then you may keep enjoying red wine as an alcoholic drink of your choice.

Green tea
Many powerful compounds are present in green tea that may help in protecting the skin from aging and damage. These compounds are referred to as catechins and they help in improving your skin health in various ways. Similar to several other foods that contain antioxidants, green tea may also help in protecting your skin against damage from ultraviolet rays of the sun. In a study, it was found that daily consumption of green tea can decrease redness from exposure to the sun by about 25 percent in 60 females. It also helps in improving the roughness, moisture, elasticity, and thickness of the skin. However, you should avoid drinking green tea with milk as it may decrease the effectiveness of antioxidants present in green tea.

What kind of skincare product ingredients will negatively impact our skin flora?
The ingredients in cosmetic products that may negatively impact the skin florae include aluminium powder, coal tar, bismuth oxychloride, formaldehyde, parabens, nanoparticles, talc, mineral oil, propylene glycol and thimerosal.
The ingredient that is present in antibacterial hand cleansers that negatively impacts skin microflorae is triclosan.

A study published in the International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research mentioned that a synthetic cosmetic contains seven ingredients in the form of water, preservatives, emulsifiers, colours, thickeners, stabilizers and fragrances. The study states that preservatives may remain active on the skin for a long time and they may alter the resident microflorae with continued use.
The study stated that people use deodorants to reduce body odour. Most deodorants have antibacterial ingredients that act against gram-positive bacteria. However, they may shift the normal florae to gram-negative bacteria and cause infections.
Can skin microflora cause harm to us?
Microflorae present on the skin can also result in non-infectious and infectious skin conditions that affect the hair follicles, epidermis, subcutis and dermis.
While commensals do not cause any harm in most individuals, they may result in minor diseases in some people or even serious disease in others. The below-mentioned factors tend to turn skin microflorae into pathogens:
- A breach in the physical skin barrier as a result of injury, skin disease (for instance, dermatitis) or an invasive medical device (for instance, a central venous line)
- Medicine to suppress the immune system
- Suppression of the immune system due to HIV, infection or cancer
- Age (both very old or very young age)
- Genetic factors of an individual
References
https://www.dermnetnz.org/cme/bacterial-infections/corynebacteria/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/microorganisms-found-on-the-skin/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/coagulase-negative-staphylococci/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/pityriasis-versicolor/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/malassezia-folliculitis/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/seborrhoeic-dermatitis/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/malassezia-infections/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11206278_Cosmetics_What_is_their_influence_on_the_skin_microflora
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2746716/
https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/demodex/
https://www.skinvitality.ca/beautiful-skin-qualities/
https://www.verywellhealth.com/whats-the-difference-between-healthy-and-unhealthy-skin-1069530
https://www.brainz.org/10-signs-poor-skin-health/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3655727/
https://www.mindbodygreen.com/0-23996/your-skin-microbiome-why-its-essential-for-a-healthy-glow.html
https://greatist.com/live/skin-microbiome-how-to-cultivate-good-skin-bacteria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25291137
https://waojournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40413-017-0160-5
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/phpp.12334
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19203862
https://www.hyperbiotics.com/blogs/recent-articles/natures-secret-to-beautiful-skin-meet-your-skin-microbiome
https://www.calmeats.com/blog/what-you-put-on-your-body-matters
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18489300
https://innovareacademics.in/journal/ijcpr/Issues/Vol5Issue3/718.pdf








